Weight loss has always been a challenging journey for millions of people. With rising rates of obesity and lifestyle-related illnesses, the demand for effective weight loss solutions has grown dramatically. Among the most talked-about drugs in recent years is Ozempic, along with others in its class. These medications promise fat loss, better blood sugar control, and long-term health improvements. But how safe are they? And are there natural alternatives?
This article breaks down everything you need to know about Ozempic and similar weight loss drugs—their mechanisms, benefits, risks, and ongoing research—so you can make informed decisions about your health.
Introduction to Weight Loss Drugs
The Growing Popularity of Prescription Weight Loss Medications
Obesity is linked to diabetes, heart disease, and even cancer. Traditional approaches like diet and exercise work but often provide slow results. Prescription medications like Ozempic offer faster weight loss. They provide more significant results, making them a hot topic among both doctors and patients.

What is Ozempic?
Drug Class and Medical Background
Ozempic (generic name: semaglutide) belongs to a drug class known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. Originally designed for type 2 diabetes, it helps regulate blood sugar while also leading to significant fat loss.
FDA Approvals and Off-Label Use
The U.S. FDA approved Ozempic in 2017 for type 2 diabetes. However, its weight-loss potential led to the development of Wegovy, another form of semaglutide specifically approved for obesity management.
How Ozempic and Similar Drugs Work
The Role of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 stands for Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, a hormone that controls appetite, insulin secretion, and stomach emptying. Drugs like Ozempic mimic this hormone, creating a powerful effect on hunger and calorie consumption.
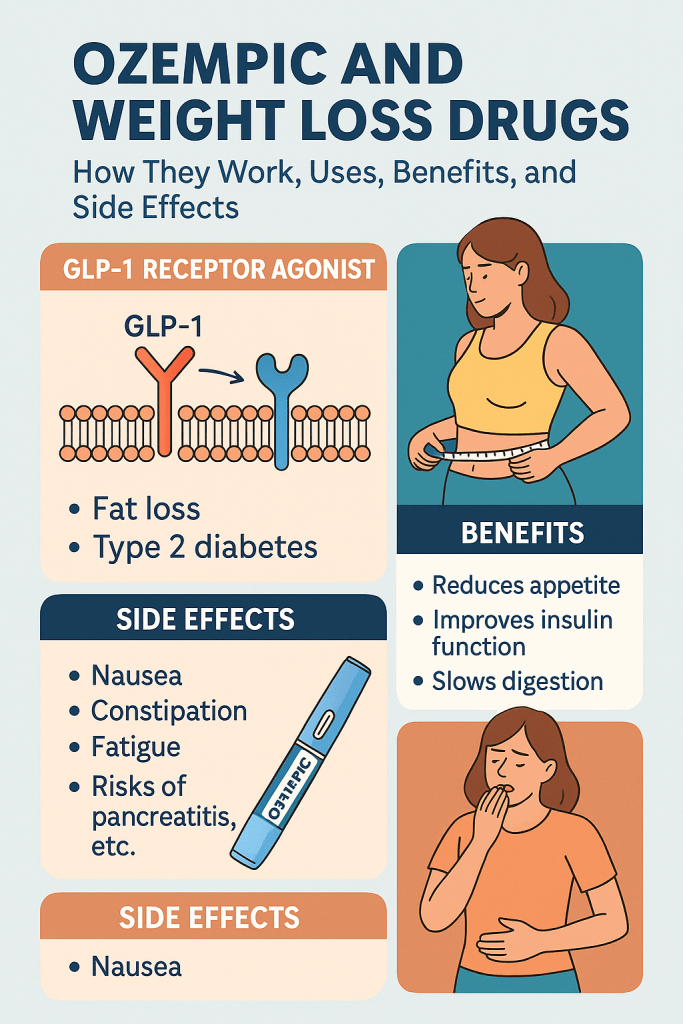
Impact on Appetite, Insulin, and Digestion
- Reduces appetite → People feel full sooner.
- Slows digestion → Prevents overeating.
- Improves insulin sensitivity → Helps with blood sugar balance.
Advantages of Using Ozempic for Fat Loss
- Effective in reducing weight: Clinical trials show an average loss of 15% of body weight.
- Improves type 2 diabetes control: Stabilizes blood sugar and reduces insulin dependence.
- Long-term health benefits: Lower risk of heart disease and better metabolic health.
Disadvantages and Side Effects
Common Side Effects
Nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and fatigue are common, especially in the first few weeks.
Serious Health Risks
Rare but concerning risks include pancreatitis, kidney issues, and gallbladder disease.
Accessibility and Cost
These drugs can be very expensive, and insurance coverage varies.
Other Drugs Similar to Ozempic
- Wegovy: Another form of semaglutide, specifically approved for weight loss.
- Mounjaro (tirzepatide): A dual GIP/GLP-1 agonist showing even greater fat loss results.
- Saxenda (liraglutide): An older GLP-1 agonist with similar effects.
Ongoing Research on GLP-1 Drugs
- Human Trials: Studies are testing semaglutide for long-term obesity and cardiovascular health.
- Animal Studies: Research explores safety, cancer risks, and metabolic improvements.
Drug and Supplement Interactions
- Prescription drugs: May interact with insulin, blood pressure medications, or blood thinners.
- Supplements: Some herbal supplements (like berberine) may amplify blood sugar effects.
Natural Alternatives to GLP-1 Drugs
Foods That Boost GLP-1 Naturally
- Fermented foods (kimchi, yogurt)
- High-fiber foods (oats, beans)
- Protein-rich meals

Lifestyle Changes for Sustainable Weight Loss
Exercise, mindful eating, and sleep optimization can mimic some GLP-1 benefits.
Herbal and Nutritional Supplements Being Studied
Berberine, green tea extract, and chromium may offer mild appetite control.
Conclusion
Ozempic and similar drugs represent a revolution in weight loss treatment, offering real hope for people struggling with obesity. They work by mimicking natural hormones to suppress appetite and regulate metabolism. However, they come with risks, high costs, and limited accessibility.
Natural approaches—like diet, exercise, and gut-friendly foods—may not provide the same dramatic results. However, they can mimic some of the benefits safely and sustainably.
If you’re considering Ozempic or similar drugs, always consult a healthcare professional to weigh the benefits against the risks.
Leave a comment